題組內容
7. A goods market is described by the following set of equations:
Y = C (Y - T (Y )) + I (r ) + G0 ,
where Y is the level of national income, and C, I, G, and T are consumption, investment, government
spending, and taxes, respectively. If we denote disposable income as 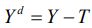 , then the consumption function can be expressed as:
, then the consumption function can be expressed as: 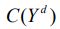 , where
, where 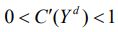 1 is the marginal propensity to consume.Investment spending is assumed to be a strictly decreasing function of the rate of interest, r:
1 is the marginal propensity to consume.Investment spending is assumed to be a strictly decreasing function of the rate of interest, r: 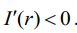 . The public sector is described by two variables: government spending (G) and taxes (T). Typically, government spending is assumed to be exogenous whereas taxes are assumed to be an increasing function of income:
. The public sector is described by two variables: government spending (G) and taxes (T). Typically, government spending is assumed to be exogenous whereas taxes are assumed to be an increasing function of income:
0 < T ''(Y ) < 1.
A money market is described by the following three equations: 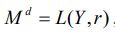 ,
, 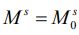 , and
, and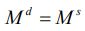 , where
, where 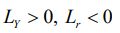 0 and the money supply is assumed to be exogenously determined by the central monetary authority.
0 and the money supply is assumed to be exogenously determined by the central monetary authority.
(c) Derive the following two comparative-static derivatives: 