活動名稱
【解題達人! We want you!】
活動說明
阿摩站上可謂臥虎藏龍,阿摩發出200萬顆鑽石號召達人們來解題!
針對一些題目可能有疑問但卻缺少討論,阿摩主動幫大家尋找最佳解!
懸賞試題多達20萬題,快看看是否有自己拿手的科目試題,一旦你的回應被選為最佳解,一題即可獲得10顆鑽石。
懸賞時間結束後,只要摩友觀看你的詳解,每次也會得到10顆鑽石喔!
關於鑽石
如何使用:
- ✔懸賞試題詳解
- ✔購買私人筆記
- ✔購買懸賞詳解
- ✔兌換VIP
(1000顆鑽石可換30天VIP) - ✔兌換現金
(50000顆鑽石可換NT$4,000)
如何獲得:
- ✔解答懸賞題目並被選為最佳解
- ✔撰寫私人筆記販售
- ✔撰寫詳解販售(必須超過10讚)
- ✔直接購買 (至站內商城選購)
** 所有鑽石收入,都會有10%的手續費用
近期考題
【非選題】
【題組】(二)承上題,會計師事務所預計與您共同檢視該捷運公司主要風險的來源,須請您協助提供資料,請 您以企業經營之角度,試列舉該公司「組織層級風險」及「作業層級風險」之來源為何。(25 分)
一、企業為健全整體內部控制制度之設計與執行,妥善之風險管理制度實為發展之重要基礎,請依據
下列各種情境回答問題:
【題組】(二)承上題,會計師事務所預計與您共同檢視該捷運公司主要風險的來源,須請您協助提供資料,請 您以企業經營之角度,試列舉該公司「組織層級風險」及「作業層級風險」之來源為何。(25 分)
【非選題】
【題組】2.本為的結果與結論為何?(200字左右)
第五大題:
請閱讀以下摘要,並回答下列的問題(15%):
PURPOSE. To compare the efficacy of behavioral activation (BA) plus low vision rehabilitation with an occupational therapist
PURPOSE. To compare the efficacy of behavioral activation (BA) plus low vision rehabilitation with an occupational therapist
(OT-LVR) with supportive therapy (ST) on visual function in patients with age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
METHODS. Single-masked, attention-controlled, randomized clinical trial with AMD patients with subsyndromal depressive
symptoms (n = 188). All subjects had two outpatient low vision rehabilitation optometry visits, then were randomized to in-home
BA + OT-LVR or ST. Behavioral activation is a structured behavioral treatment aiming to inctease adaptive behaviors and achieve
valued goals. Supportive therapy is a nondirective, psychological treatment that provides emotional support and controls for
attention. Functional vision was assessed with the activity inventory (Al) in which participants rate the difficulty level of goals and
corresponding tasks. Participants were assessed at basetine and 4 months.
RESULTS. Improvemcnts in functional vision measures were seen in both the BA + OT-LVR and ST groups at the goal level (d e
0.71; d = 0.56 respectively). At the task level, BA + OT-LVR patients showed more improvement in reading, inside-the-home tasks
and outside-the-home tasks, when compared to ST patients. The greatest effects were scen in the BA + OT-LVR group in subjects
with a visual acuity 220/70 (d = 0.360 reading; d = 0.500 inside the bome; d = 0.468 outside the home).
CONCLUSIONS. Based on the trends of the AI data, we suggest that BA + OT-LVR services, provided by an OT in the patient's
home following conventional low vision optometry services, are more effective than conventional optometric low vision services
alone for those with mild visual impairment.
(文章出處::Ashley D. Deemer, et al. (2017) Functional outcomes of the low vision depression prevention trial in age-related
macular degeneration. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 58:1514-20.)
【題組】2.本為的結果與結論為何?(200字左右)
47. 甲、乙為採分別財產制的配偶,甲死亡時留下540萬元,以遺囑全部遺贈給其好友;甲除配
偶乙之外,尚有父丙、姊丁、妹戊在世,丙合法拋棄對甲之繼承。請問戊就甲之遺產有特留
分額為多少?
(A) 45萬元
(B) 67.5萬元
(C) 90萬元
(D) 135萬元
(A) 45萬元
(B) 67.5萬元
(C) 90萬元
(D) 135萬元
【非選題】
【題組】(三)定滑輪上之大輪 A 直徑為幾公分?【5 分】
第五題:
機電設施維修廠房內經常安裝有如【圖五】所示之惠斯頓差動滑車(Weston differential pulley block),假設定滑輪上之小輪 B 直徑為 25 cm,將重物 W 拉升 18 cm 時,需要拉動鏈條 1.5 m,若施力 F 為 60 N,在
不計摩擦損失的情況下,請回答下列問題:【未列出計算過程者不予計分】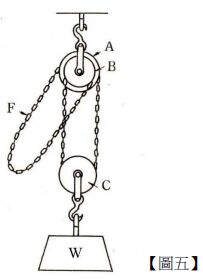
【題組】(三)定滑輪上之大輪 A 直徑為幾公分?【5 分】
【非選題】
三、若你所服務的部門主要任務在於自行發展功能性業務用途軟體。作為一個專案管理 者在軟體專案的開發選擇上那些因素會是你重要的考量因素,請依專案特性構面 (如專案重要性)、財務構面(如預期效益)及開發作業構面(如投入之專業技術) 分別加以描述。(25 分)
三、若你所服務的部門主要任務在於自行發展功能性業務用途軟體。作為一個專案管理 者在軟體專案的開發選擇上那些因素會是你重要的考量因素,請依專案特性構面 (如專案重要性)、財務構面(如預期效益)及開發作業構面(如投入之專業技術) 分別加以描述。(25 分)
17.尺度界線的敘述,下列何者錯誤?
(A)尺度界線為確定距離的位置
(B)尺度界線與視圖之輪廓線並未互相接觸,其間距應為1mm
(C)建築圖尺度單位常用公厘表示
(D)表示中心點的位置時,尺度界線應以中心線代替,避免誤解
(A)尺度界線為確定距離的位置
(B)尺度界線與視圖之輪廓線並未互相接觸,其間距應為1mm
(C)建築圖尺度單位常用公厘表示
(D)表示中心點的位置時,尺度界線應以中心線代替,避免誤解
93. 應對執法機關詢問的三種可取方式是什麼?
(A) 儘量配合執法機關詢問。
(B) 盡可能迅速且徹底地回應所有正式的資訊要求,除非可以且應當提出有效的異議。
(C) 確保將所有的書面和口頭通訊進行集中。
(D) 通過盡可能拒絕所有詢問和要求來保護資訊不被無故公開。
(A) 儘量配合執法機關詢問。
(B) 盡可能迅速且徹底地回應所有正式的資訊要求,除非可以且應當提出有效的異議。
(C) 確保將所有的書面和口頭通訊進行集中。
(D) 通過盡可能拒絕所有詢問和要求來保護資訊不被無故公開。