試卷測驗 - 110 年 - [無官方正解]110 國立臺灣大學_碩士班招生考試_部分系所:生物化學(A)#102083-阿摩線上測驗
小咕利剛剛做了阿摩測驗,考了100分
1. What type of glycosidic linkage does a sucrose molecule (as shown below) have?

(A) β-1,3
(B) β-1,2
(C) α-1,3
(D) α-1,2
(E) α-1,4
15. Serine can be converted directly into pyruvate. The reaction, catalyzed by serine dehydratase, requires the
coenzyme:
(A) pyridoxal phosphate (PLP).
(B) biotin.
(C)  .
.
(D) tetrabydrofolate.
(E) nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD).
第26至50題每題2.5分
Use the five amino acids labelled as a-e in the table below to answer the questions 26~28.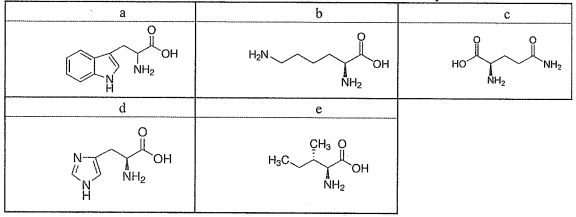
29. Edman degradation of a polypeptide yielded a chemical structure as follows. What kind ofamino acid is located
at the N-terminus of this polypeptide?

(A) Cys
(B) Phe
(C) Ile
(D) Leu
(E) Tyr
31 . The following data were obtained in a study of an enzyme known to follow Michaclis-Menten kinetics:
Substrate added
(umol/min) (mmol/L)

The Km for this enzyme is approximately:
(A) I mM.
(B) 2 mM.
(C) 1,000 mM.
(D) 4 mM.
(E) 6 mM.
32. Carbonic anhydrase has two substrates, carbon dioxide and bicarbonate, which are both converted to carbonic
acid. Kinetic data for each is given below. While determining the kinetics of  as a substrate, how would
the addition of CO2 effect the reaction if the rate were measured by the disappearance of bicarbonate?
as a substrate, how would
the addition of CO2 effect the reaction if the rate were measured by the disappearance of bicarbonate?

(A) CO2 would increase the activity of the enzyme.
(B) CO2would cause an apparent decrease in the Km for 
(C) CO2 would act as a competitive inhibitor.
(D) CO2 would act as a noncompetitive inhibitor.
(E) CO2 would act as an umcompetitive inhibitor.
33. The catalytic mechanism below is an example of:

(A) covalent nucleophilic catalysis.
(C) specific base catalysis.
(B) covalent electrophilic catalysis.
(D) general base catalysis.
(E) low barrier hydrogen bond catalysis.
35. Which of the following statements concemning the free energy change (△G) is false?
(A) The energy change for a reaction depends only on the initial and final states, and is independent of the
path taken.
(B) A spontaneous reaction is one in which energy is absorbed.
(C) The standard state usually used in biochemistry  includes all concentrations at 1 M, except for [H+],
which is
includes all concentrations at 1 M, except for [H+],
which is  M.
M.
(D) The AG values for giycolytic reactions at physiological conditions may be exergonic, even though the  at "standard" conditions, may be endergonic.
at "standard" conditions, may be endergonic.
(E) None is false.
39. Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) also involves in the formation of acetyl-CoA, in which TPP has to be
deprotonated first and then attacks one site of pyruvate. Please identify which site.

(A) Site A
(B) Site B
(C) Site C
(D) Site D
(E) Site E
46. Besides B-oxidation for lipid ietabolism, there are other ways to catabolize lipid. Which statement is correct?
(A) There is NAD-dependent β-oxidation for lipid metabolism in peroxisomes.
(B) The B-oxidation in peroxisomes uses O2 to oxidize lipid and produces H2O2.
(C) Branched-chain lipids are degraded via co-oxidation.
(D) a-Oxidation is the main route to produce dicarboxylic acids.
(E) None of the above.
48. Thymidylate synthase methylates dUMP at 5 position to make dTMP. The methyl donor is _________.
(A) S-adenosylmethionine
(B)  methylene-THF
methylene-THF
(C) 5-methyl-THF
(D) taurine
(E) creatine.