

- ✔懸賞試題詳解
- ✔購買私人筆記
- ✔購買懸賞詳解
- ✔兌換VIP
(1000顆鑽石可換30天VIP) - ✔兌換現金
(50000顆鑽石可換NT$4,000)
- ✔解答懸賞題目並被選為最佳解
- ✔撰寫私人筆記販售
- ✔撰寫詳解販售(必須超過10讚)
- ✔直接購買 (至站內商城選購)
近期考題
(A)我们真诚地希望常昊夺取世界冠军之后再接再厉,不断带给人们惊喜。
(B)我国正在紧锣密鼓地进行“神舟”六号太空飞行的各项准备工作。
(C)市中心许多商业广告牌被庆祝反法西斯战争胜利日的宣传画取而代之。
(D)近十多年来,我国的城市“夜景观”建设琳琅满目,发展十分迅速。
四、Viết văn(30 分)
19. 如圖所示電路,VA、VB為同阻值之電阻性負載,當開關閉合後,則VA及VB的關 係為何?

(A) V A =0 V
(B) V B =0 V
(C) VA =VB =12 V
(D) VA =12 V A ,VB =0 V
四、薄壁箱型斷面尺寸如圖四所示,假設斷面材料性質 G,斷面預期受到之扭力 T、垂直剪力 V、橫向水平剪力 H。請試述下列關於剪力流之問題;(作答過程可維持參數符號或以下列代表值進行計算,G=10 GPa、
T=1 kN-m、V=H=1 kN、h=1 m、t=10 cm)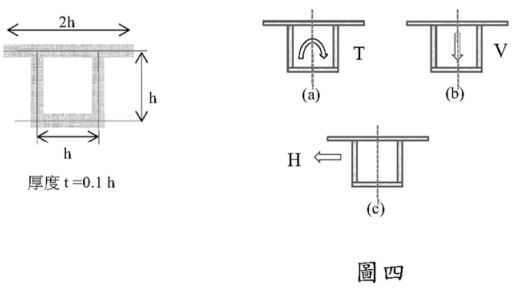
【題組】(二)斷面僅受到圖四(b)垂直剪力時,計算剪力流分布趨勢、方向及標示出最大值位置。(10 分)
【題組】2. Wenn wir uns getroffen haben, haben wir ___________ immer über Kunst _________________.
25. Consider the following gas samples:

Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE?
(A) Assuming identical intermolecular forces in the two samples, sample M should be more
nearly ideal than sample N.
(B) The root-mean-square velocity of molecules in sample M is twice as large as the root-
mean-square velocity of molecules in sample N.
(C) The average kinetic energy of the molecules in sample M is twice the average kinetic
energy of the molecules in sample N.
(D) The fraction of molecules in sample M having kinetic energies greater than some high
fixed value is larger than the fraction of molecules in sample N having kinetic energies
greater than that same high fixed value.
(E) The volume of sample M is twice the volume of sample N.