題組內容
1. The following figure shows the IEEE 754 standard for floating-point representation of both single-precision (short) and double precision (long) formats to represent a regular filoating number t1.fx2'
where 1.f is called significand and e is the exponent, and other special numbers.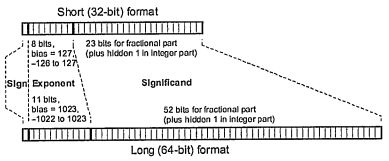
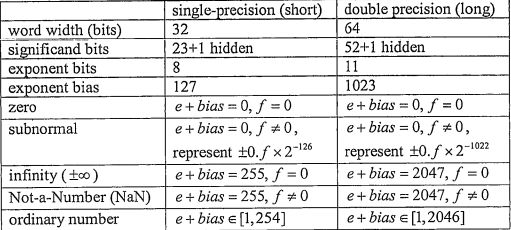
1.4 What is the minimum magnitude of ordinary numbers (i.e, other than zero) in single precision foating-point representation? Express your answer in format of x..cx---xx× where x∈ (0,1) and e is the decimal value of the exponent.
where x∈ (0,1) and e is the decimal value of the exponent.