載入中..請稍候..
【試題】靜謐日常
【說明】
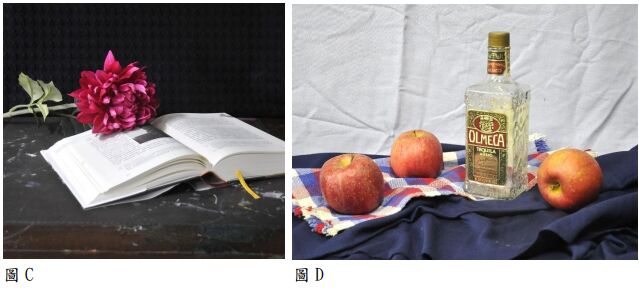
一、請以圖 A 或圖 B 為主題,完成一件素描作品。
二、下面四張圖片,有電話、石膏像、花、書本、酒瓶、蘋果、桌布共 7 種物件,
皆須入畫,其中物件數量、光影、位置、方向、比例可依需求予以增減或改變。
但是不得添加試題以外之物件。
三、請以寫實技法呈現。限單色手繪,且為現場能夠乾燥固著之媒材。
四、以下為高一個案資料簡述:
(一)生理與心理
1.個案國中為數理資優班,成績優異。九年級時因焦慮、憂鬱分別至精神科及心理諮商診所就醫與心理諮商,迄今更換過3位醫師及2位諮商心理師。個案未被列入轉銜輔導系統,近期導師轉介至輔導室。
2.個案進入高中後持續穩定回診服藥,但認為自費心理諮商無用不再延續,但向導師表達願意與輔導教師晤談。個案對精神科用藥及副作用頗有研究,喜歡回診時與醫師討論藥物,並評價醫師的優劣處。
(二)家庭狀況
1.個案為獨生子,案父於個案國八時投資失敗,對此自責不已。案母於個案國小三年級時因職場壓力大,出現憂鬱及焦慮症狀,曾吞藥自殺,目前有酗酒行為且就醫不穩定。案母情緒低落時會尋求個案安慰,個案對此感到擔心,曾在學校時躲在廁所回訊關懷及安撫案母。
2.案父對案母就醫不穩定感到無力,且認為案母的情緒會拖累個案,案父曾與導師會談時掩面痛哭,覺得自己快被拖垮。
3.個案第一次定期考前一日,因自覺複習及解題速度太慢,將搞砸定期考,向案母表示,若成為失敗者乾脆吞藥自殺。個案要求父母幫助自己說服醫師施打長效針劑或其他診治方式。(三)在校適應
1.個案對師長親切有禮,認為同學大多膚淺不須深交,從小無知心朋友。國中起下課時間幾乎都在念書、玩手機或睡覺。與高中同學關係疏離,曾於分組活動時落單。
2.個案開學迄今上課認真,但小考狀況不穩定,第一次定期考班排倒數,公布成績後情緒大受影響,已請假休息兩日。
根據以上描述:
(三)除了個別晤談之外,您還會有哪些處遇?
(二)請您依據您熟悉的諮商取向,提出初步的個案概念化以及諮商介入。
(C)
Soil organic carbon (SOC) plays a pivotal role in maintaining soil health, influencing its structure, fertility, and water retention capabilities. Beyond these agronomic benefits, SOC serves as a significant carbon reservoir, sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO₂) and thereby mitigating climate change. The equilibrium of SOC within the soil matrix is governed by a dynamic interplay between carbon inputs—primarily from plant photosynthesis—and outputs resulting from microbial decomposition and respiration.
The sequestration of carbon in soil is contingent upon several factors, including climatic conditions, soil mineralogy, and landuse practices. Climatic variables such as temperature and precipitation exert considerable influence over SOC dynamics. Elevated temperatures can accelerate microbial activity, leading to increased decomposition rates and subsequent CO₂ emissions. Conversely, higher precipitation levels may enhance plant productivity, thereby augmenting carbon inputs to the soil. However, excessive moisture can also create anaerobic conditions that slow decomposition, potentially leading to greater SOC accumulation. Soil mineral composition is another critical determinant of SOC storage. Research indicates that certain minerals, such as iron oxides and aluminous clays, have a pronounced capacity to adsorb organic carbon, thereby stabilizing it within the soil matrix. Soils rich in these minerals often exhibit higher SOC content due to the strong associations formed between organic matter and mineral surfaces, which protect organic carbon from microbial degradation.
Land-use practices significantly impact SOC levels. Agricultural activities, particularly those involving intensive tillage, can disrupt soil structure, leading to increased oxidation of organic matter and a consequent decline in SOC stocks. Conversely, adopting practices such as reduced tillage, cover cropping, and the incorporation of organic amendments can enhance SOC sequestration. Furthermore, the implementation of regenerative agricultural techniques has been shown to improve soil health and increase carbon storage, with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence aiding in the monitoring and verification of these practices.
The stability of SOC is not immutable; it is susceptible to perturbations from both anthropogenic and natural factors. For instance, alterations in land use, climate change, and soil management practices can disrupt the delicate balance of carbon inputs and outputs, leading to either the sequestration or release of carbon. Notably, studies have highlighted that certain ecosystems, such as the Arctic tundra, which historically served as carbon sinks, are transitioning to carbon sources due to rising global temperatures. In summary, SOC is a linchpin in the global carbon cycle, with profound implications for soil health and climate regulation. A comprehensive understanding of the myriad factors influencing SOC dynamics is essential for developing effective land management strategies aimed at enhancing carbon sequestration and mitigating the adverse effects of climate change.
*** Your writing should follow the format of a letter, signed at the end with either "Mary" or "Peter." Avoid including any personal information, such as your real Chinese or English name. Dear Colleague, I hope you’re doing well. I’m reaching out because I feel overwhelmed by the idea of integrating AI into my English classroom. While I see its potential, I have no idea where to start since I am not that tech-savvy. My biggest concern is teaching writing. As usual, I guide students through brainstorming, drafting, revising, and editing. How does AI fit into this process without making students over-rely on it? Should I allow them to use AI for idea generation or just for revising their final drafts? I also need guidance on AI writing tools. There seem to be so many—ChatGPT, Grammarly, QuillBot, etc.—but I don’t know which are the most effective or appropriate for high school students. Are there any tools specifically designed for educational settings that promote learning rather than shortcutting the process? Finally, how can AI help with correcting and revising? I spend hours giving feedback on grammar, structure, and clarity. Can AI assist with this without replacing the valuable learning that comes from teacher and peer feedback? I’d really love any advice or resources you can share. Right now, I feel lost, but I want to use AI in a way that benefits my students. Best regards, Lisa (a teacher eager to learn)
45. Which of the following can be reasonably inferred from the passage? (A) If global warming continues unchecked, some ecosystems may become net contributors to carbon emissions. (B) Disrupting the soil through mechanical means generally enhances its ability to store organic carbon. (C) Global warming will strengthen SOC stability by enhancing soil mineral composition. (D) The Arctic tundra has been functioning consistently as a significant reservoir for sequestering carbon.
44. Which of the following is not identified in the passage as a factor that contributes to the increase of soil organic carbon (SOC)? (A) The presence of soil minerals such as iron oxides and aluminous clays that stabilize organic matter (B) Limited oxygen availability in waterlogged soils that slows down decomposition (C) Warmer temperatures that stimulate microbial activity (D) Increased plant productivity resulting from higher levels of precipitation
This is a large modal.